The Robotics Roundup is a weekly newspost going over some of the most exciting developments in robotics over the past week.
In today’s edition we have:
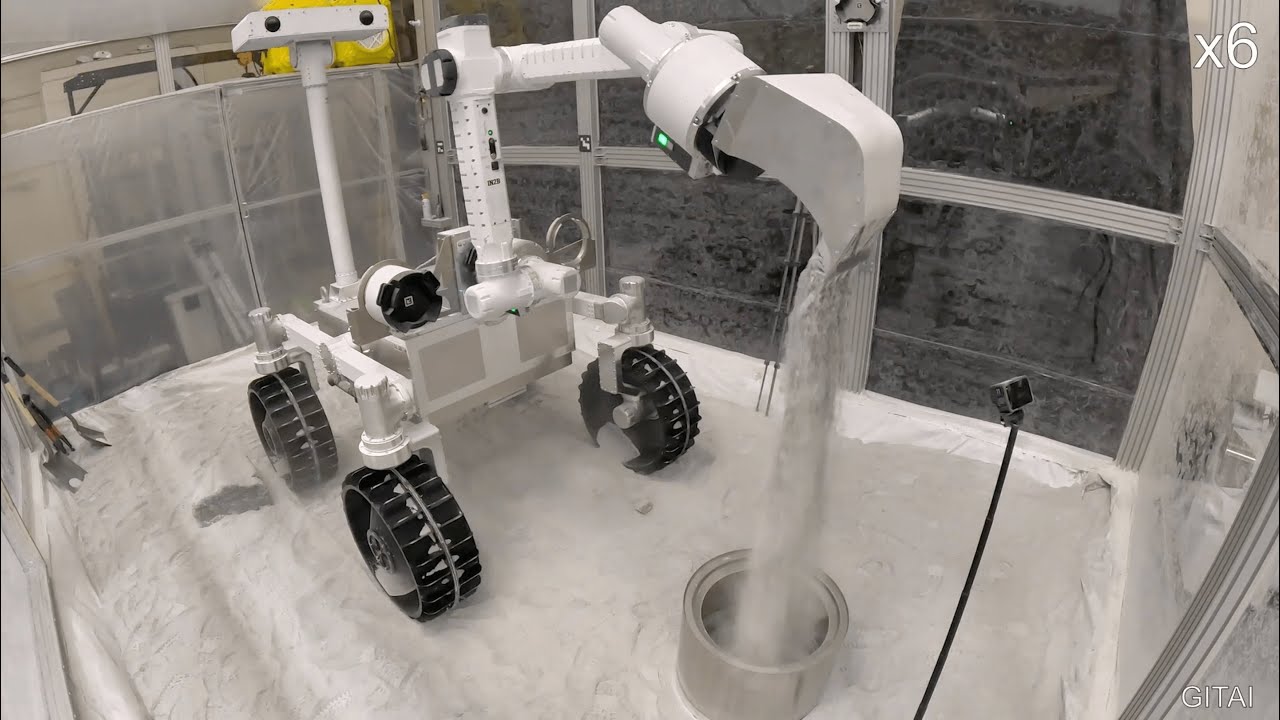
- GITAI Successfully Demonstrates Lunar Manipulator and Rover in Simulated Regolith Chamber
- Swarming microrobots self-organize into diverse patterns
- Team from KAIST wins Quadruped Robot Challenge of UK
- Spot Levels Up | Boston Dynamics
- The Dingo | A Low Cost, Open-Source Robot Quadruped
GITAI Successfully Demonstrates Lunar Manipulator and Rover in Simulated Regolith Chamber
GITAI, a company focused on providing advanced labor solutions for lunar and Martian infrastructure development have conducted various tests and demonstrations, including environmental assessments in simulated space conditions and successful lunar base construction demonstrations. Recently, they established a regolith chamber facility at their USA office and performed comprehensive testing of their inchworm-type robotic arm and Lunar Robotic Rover. The robots flawlessly executed tasks such as sampling regolith and stones, inchworm arm walking, and rover locomotion.
Swarming microrobots self-organize into diverse patterns
Researchers from Cornell University and the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems have discovered an efficient method to expand the collective behavior of swarming microrobots. By mixing different sizes of micron-scale robots, they can self-organize into diverse patterns that can be manipulated using a magnetic field. This technique has potential applications in targeted drug release, where microrobots can transport and release pharmaceutical products in the human body. The study, titled “Programmable Self-Organization of Heterogeneous Microrobot Collectives,” was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The researchers used 3D-printed polymer discs coated with a ferromagnetic material and employed external oscillating magnetic fields to control the robots’ movements and interactions. By changing the magnetic field, they could influence the swarm’s behavior, including changing its shape, clustering microrobots together, and capturing and expelling external objects. The study’s findings provide insights into developing more complex collective behaviors in microrobots.
Team from KAIST wins Quadruped Robot Challenge of UK
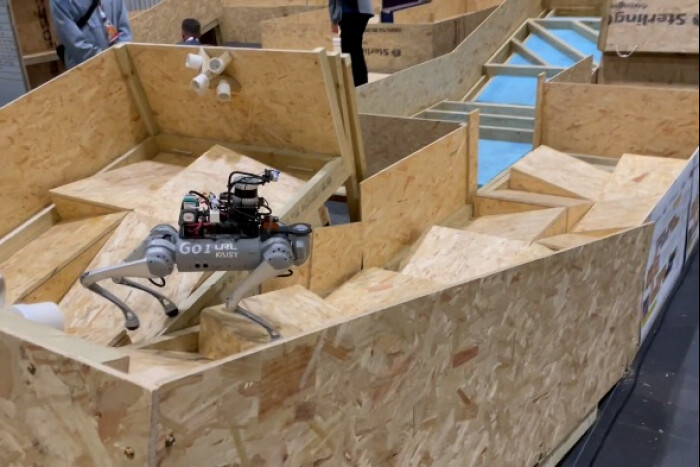

The team from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) has emerged as the winner of the Quadruped Robot Challenge held in the UK. Led by Professor Hyun Myung from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering, the Urban Robotics Lab team secured victory at the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers’ International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Their AI-based self-walking robot, DreamWaQ, achieved an impressive overall score of 246, surpassing the second-place Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) by more than four times. The scoring was based on the robot’s performance in various sections, including simulated sandy and muddy terrains. DreamWaQ also demonstrated superior speed, completing all five sections in 41 minutes and 52 seconds, outperforming the average completion time of other participating teams, which was 49 minutes.
Spot Levels Up | Boston Dynamics
Spot, a leading robot in the mobile robotics market, is introducing new features and hardware to enhance its inspection capabilities. The software update focuses on improving thermal, visual, and acoustic inspections, allowing users to capture multiple regions of interest, compare temperatures, and set alerts for abnormalities. Spot can now perform gauge reading tasks using computer vision, eliminating the need for manual monitoring. The integration of acoustic imaging enables the detection and visualization of air and gas leaks. The Scout software provides mission editing, scheduling, and real-time data reviews. On the hardware side, Spot has a new audio and visual signaling system, including safety lights, a buzzer, and a speaker, enhancing safety in industrial settings. A physical emergency stop button has been added for increased safety, along with improved behaviors on slippery surfaces and the ability to detect moving objects. Additionally, Spot’s autonomous manipulation capabilities now include the ability to autonomously open doors during missions. The ongoing collaboration and feedback aim to develop next-generation robots and solutions for safer and more productive operations.
The Dingo | A Low Cost, Open-Source Robot Quadruped
Introducing the Dingo Quadruped, a low-cost robot designed for research purposes and easy modification with additional actuators and sensors. The Dingo is an open source project built upon the Stanford Pupper and notspot pltforms, with significant modifications and integration into ROS 1 Noetic.