Kinematics Control of Continuum Robots Based on Screw Theory
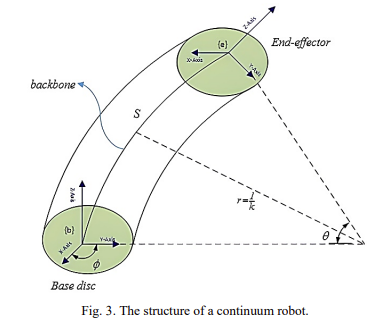
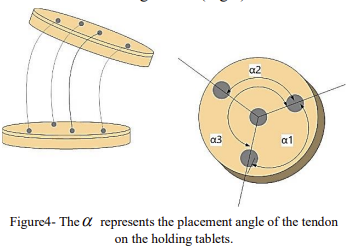
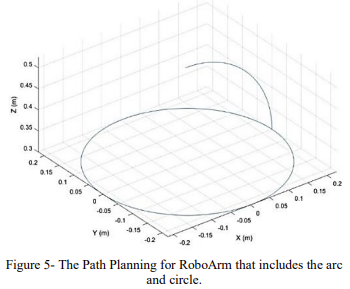
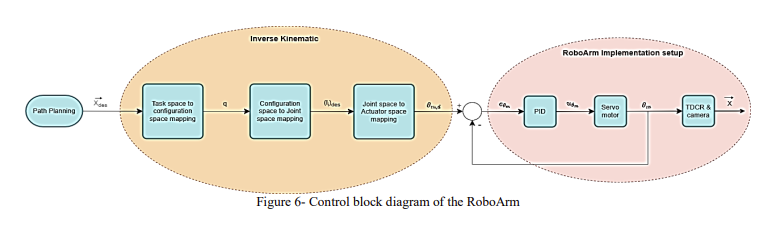
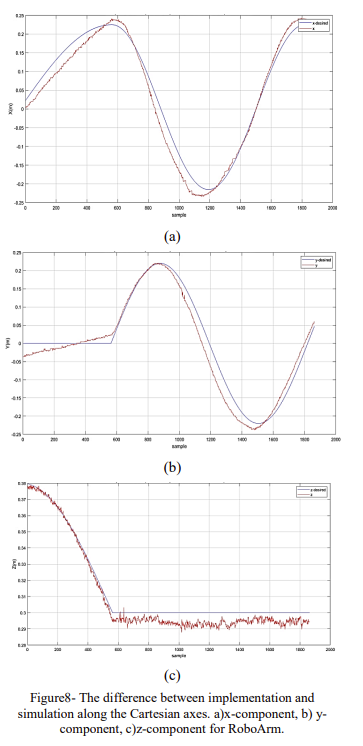
Abstract: Controlling continuum robotic arms presents significant challenges due to their highly nonlinear nature and inherently uncertain and complex structure. This complexity affects the application of continuum arms in various areas such as routing, maneuvering on complex paths, and other applications. This paper addresses a real-time kinematic control of continuum robotic arms using screw theory to develop a controller that offers accuracy, speed, and low computational load for real-time implementation. The inherent flexibility and nonlinear nature of these arms complicate precise position control. To overcome these challenges, we use a PID controller, enhancing the robot’s position control capabilities. Experimentally validated results for the designed path demonstrate the controller’s effectiveness in improving path tracking and real-time control performance. This controller was implemented on the actual RoboArm system, achieving a 6cm error.
Powered by DYNAMIXEL
Full Research Paper: Kinematics Control of Continuum Robots Based on Screw Theory
All Credits Go To: Saeedeh Shekaria, Arman Gholibeikian, S. Ali A. Moosaviana; and the Center of Excellence in Robotics and Control, Advanced Robotics and Automated Systems (ARAS) Lab., Department of Mechanical Engineering K. N. Toosi University of Technology Tehran, Iran
ROBOTIS e-Shop: www.robotis.us
DYNAMIXEL Page: www.dynamixel.com
DYNAMIXEL LinkedIn: DYNAMIXEL | LinkedIn